Where is SPICE and Solar Orbiter?
You can see where Solar Orbiter is right now here.
SPICE and Solar Orbiter science goals
Let's have a look at the main mission goals, and how SPICE will help to answer these: Solar Orbiter addresses central solar physics questions such as what drives the solar wind, why does solar activity change with time, how are particles and transient interplanetary disturbances moving in the solar wind.
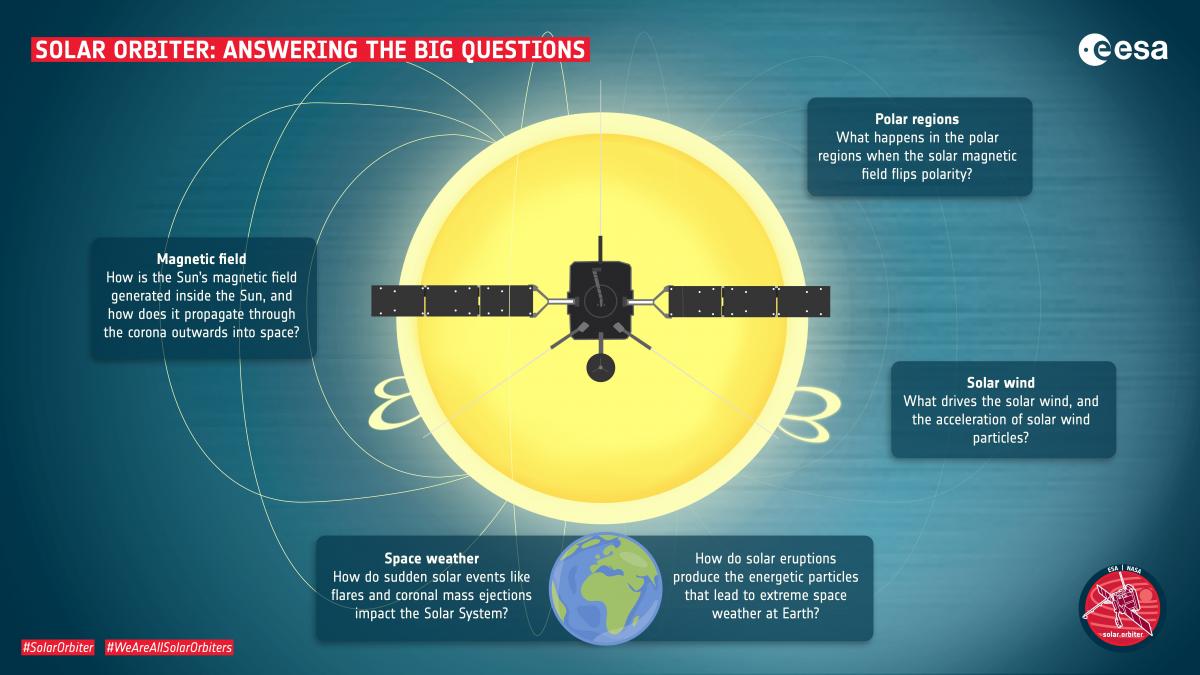
The spacecraft has a unique combination of instruments, that either measures everything around the probe (in situ observations) or far from it (remote-sensing observations). A combination of all this is important and unique at such distances from the Sun (42 million kilometres – within the orbit of planet Mercury at its closest).
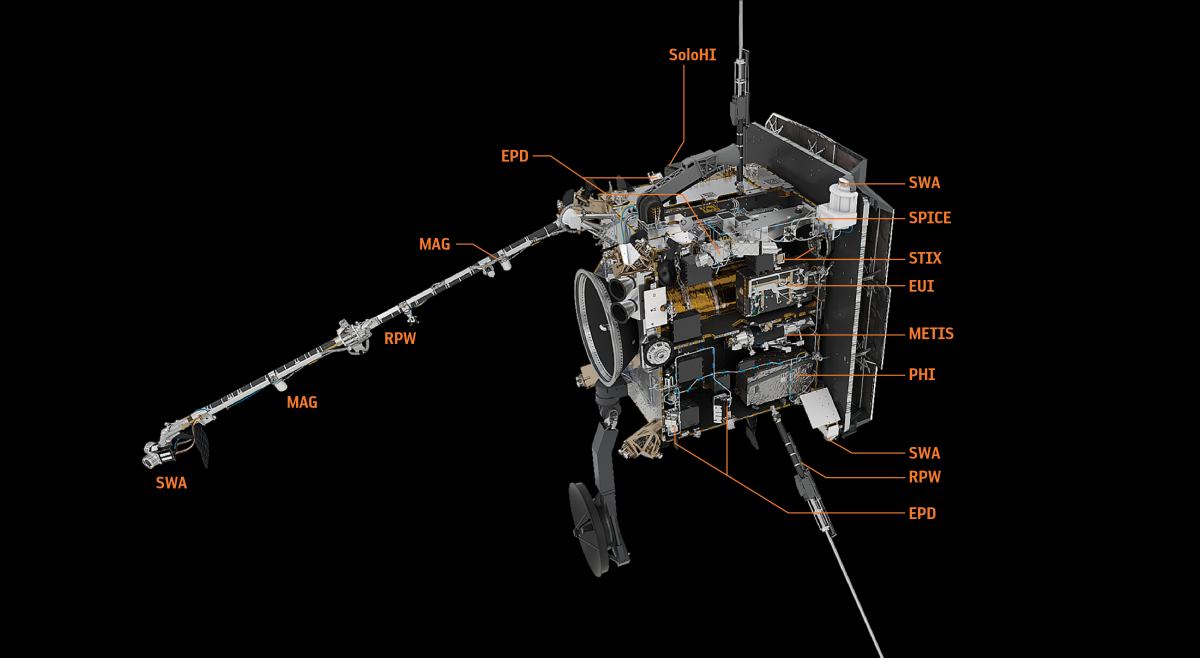
Working with other instruments
Because SPICE can remotely characterize the plasma properties of the Sun's corona, it will enable matching in situ composition signatures of solar wind streams to their source regions on the Sun's surface. So, it's an essential instrument to make the connection between what is seen at the Sun and what is seen away from it!
It is also essential for SPICE to work with other instruments. For example, the instrument PHI, that will measure the magnetic field of the Sun's surface, will help know what kind of active regions we will be studying. EUI, the Extreme-UV telescope, will help image the regions that we will look at. STIX, that detects X-rays, will help us know what kind of plasma we are studying during extreme solar events.
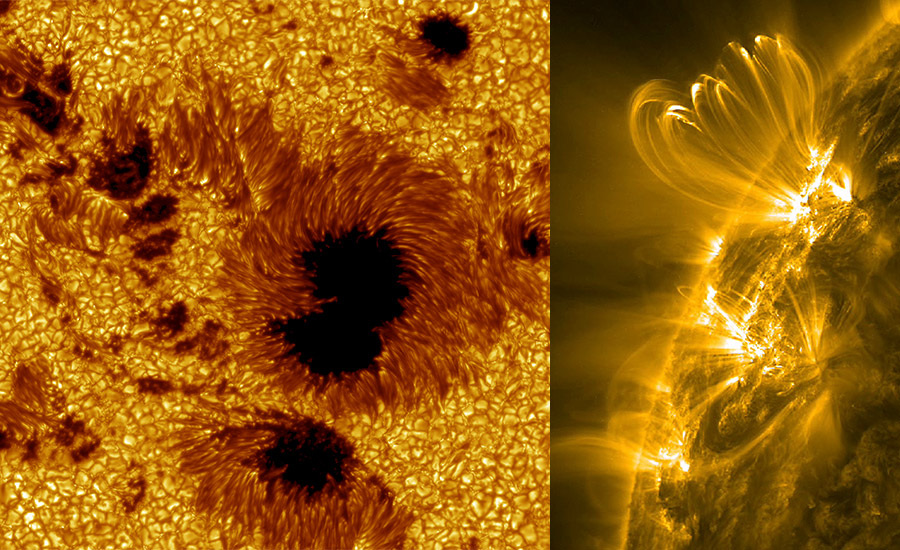
Working with in situ instruments that measure the space environment of the probe, SPICE will answer many questions, including how events seen at the Sun transforms the heliosphere, this big magnetic bubble in which planets of the solar system travel. For example, the SWA instrument will measure the properties of the plasma, that SPICE will detect at the Sun from far away.
Solar Orbiter is therefore the swiss-army knife of solar physics and heliophysics, with many tools to study the Sun and its surroundings, while flying close to our star!
